| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- Andrew Ng
- #define
- Greedy
- const
- 기계학습 기초
- algorithm
- #endif
- 본즈앤올
- compile time constants
- 단항연산자
- 나동빈님
- CLion
- regression problem
- 코드블럭 오류
- 코딩테스트
- standford University
- Machine Learning
- sizeof()
- decimal
- 프로그래밍
- 홍정모님
- Runtime constants
- 학습 알고리즘
- 형변환
- classification problem
- coursera
- 연산자
- C++
- 이코테
- 기계학습
- Today
- Total
wellcome_공부일기
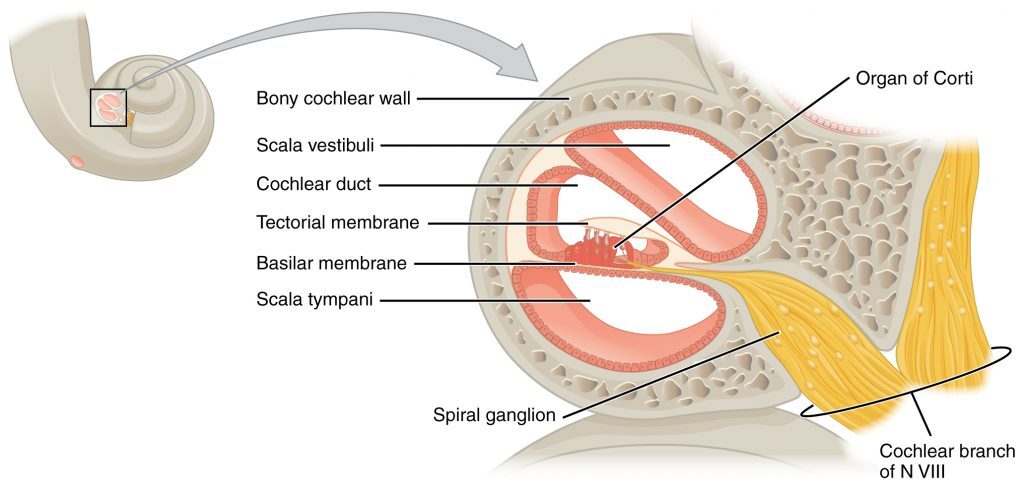
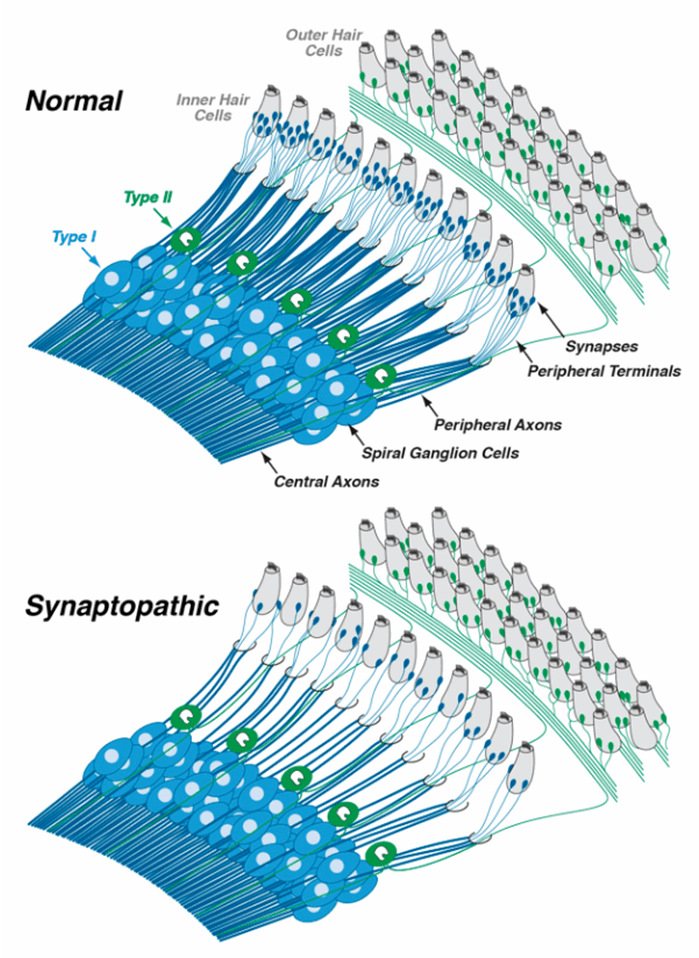
SGNs 구조 본문
Spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs)?
In the auditory system, spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs) are bipolar neurons that transfer auditory signals from auditory hair cells to the cochlear nucleus in the brainstem (Echteler, 1992; Nayagam et al., 2011).
Spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs), the primary auditory neurons. Type I SGNs comprise 90 to 95% of the SGN population and 10 to 20 of these neurons extend single, unbranched, myelinated neurites to exclusively innervate a single inner hair cell (IHC).
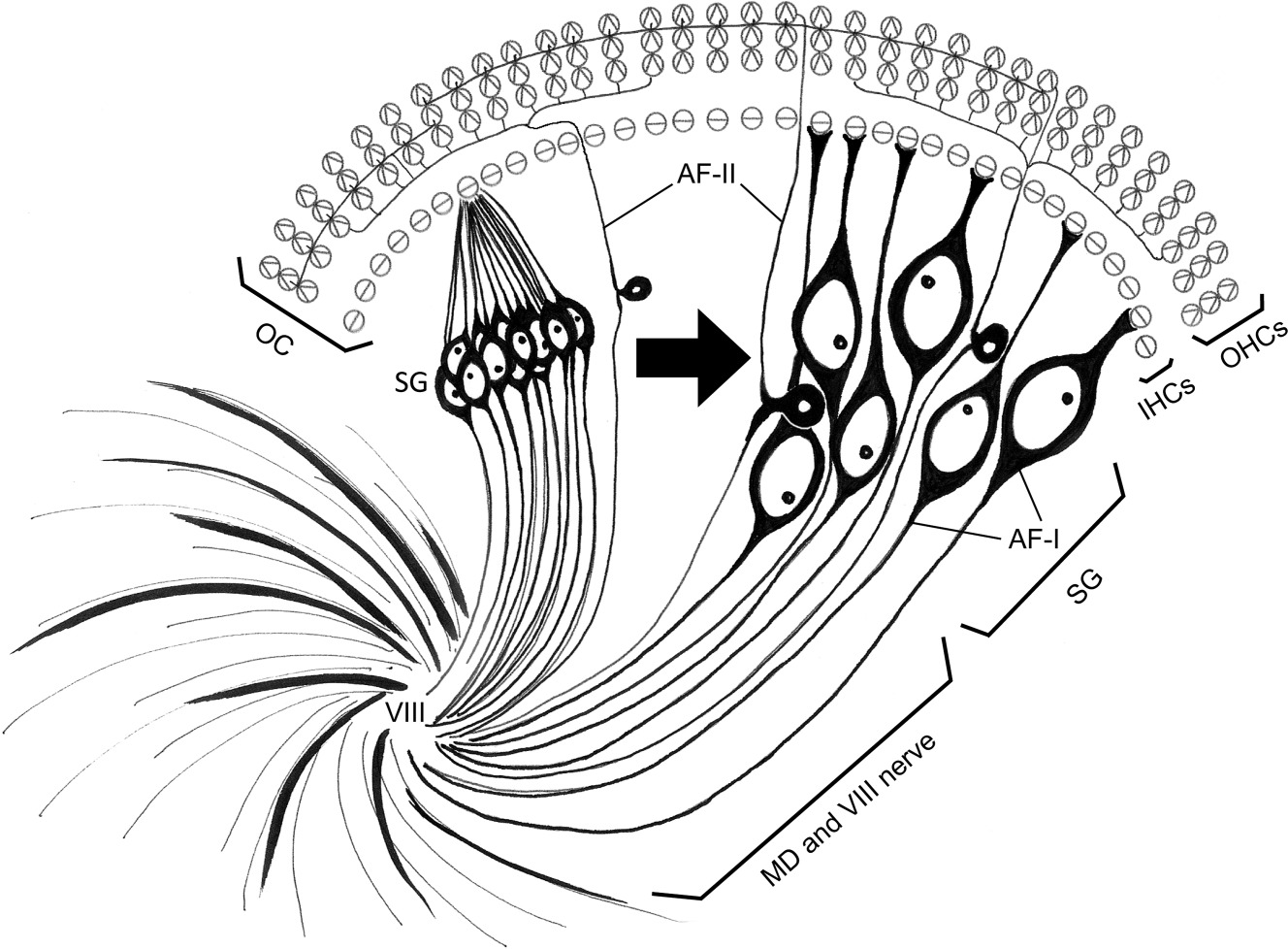
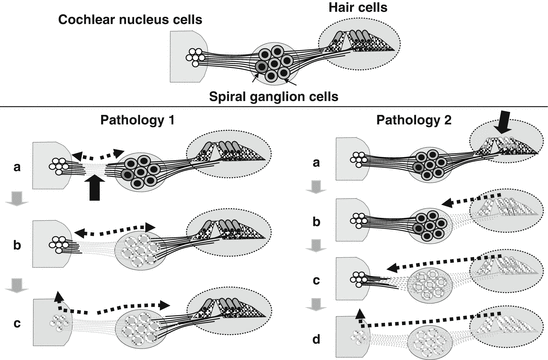
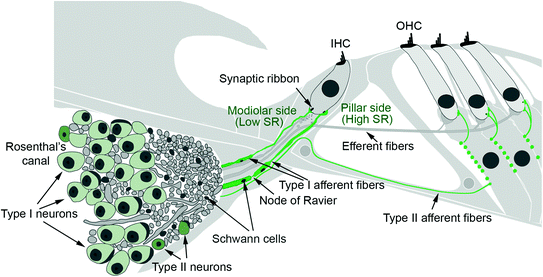
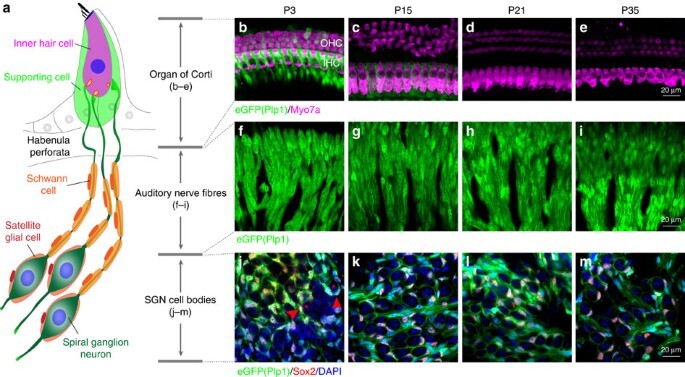
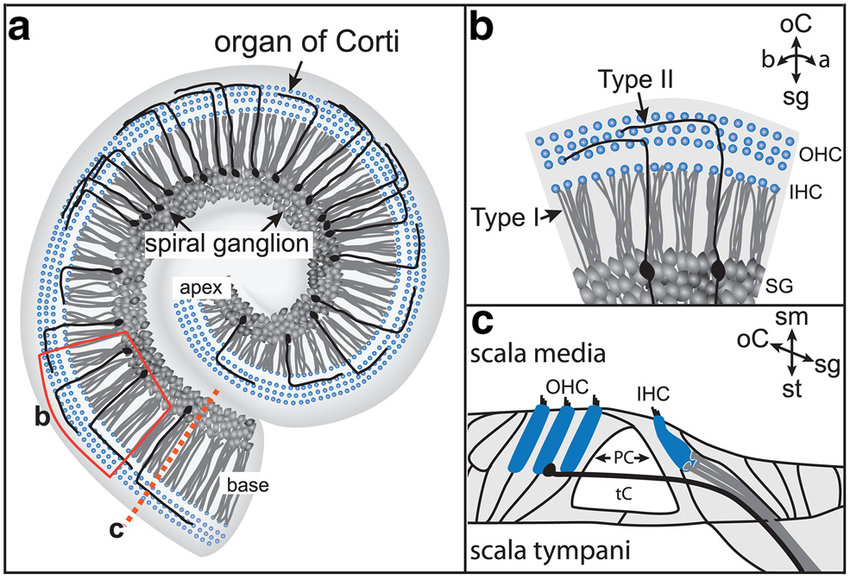
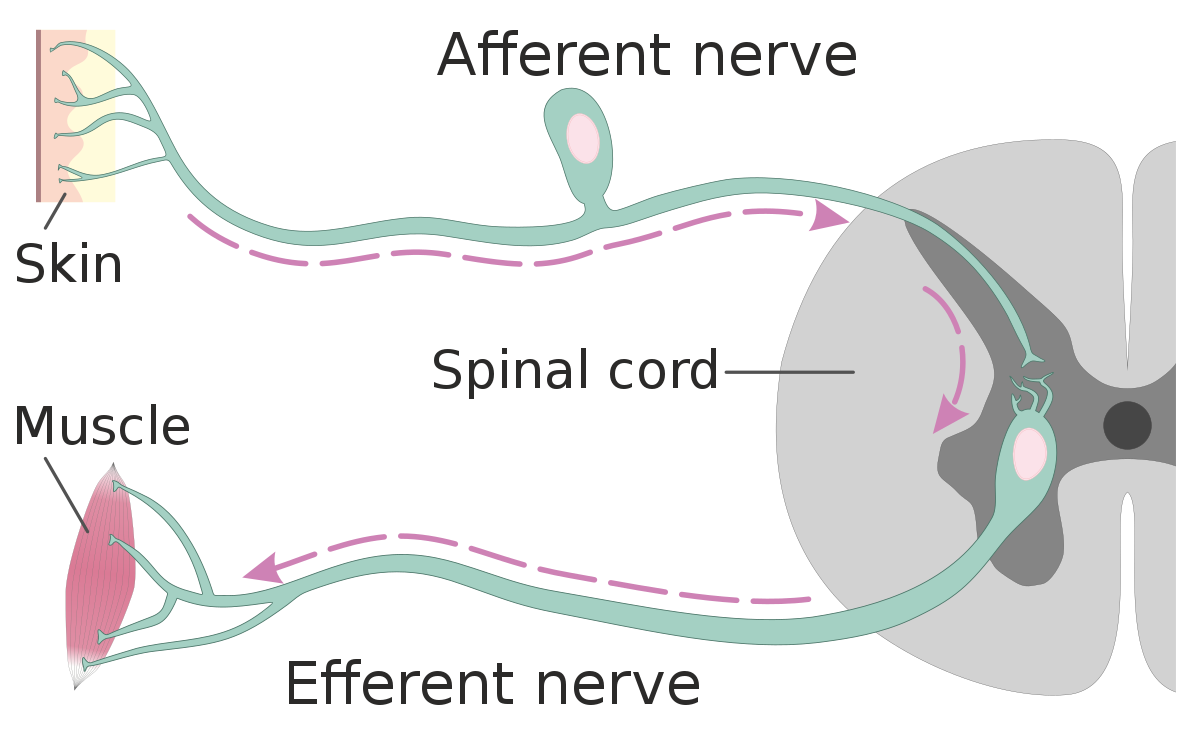
Afferent and Efferent Difference?
Afferent nerve fibers are the axons (nerve fibers) carried by a sensory nerve that relay sensory information from sensory receptors to regions of the brain. Afferent projections arrive at a particular brain region. Efferent nerve fibers are carried by efferent nerves and exit a region to act on muscles and glands.
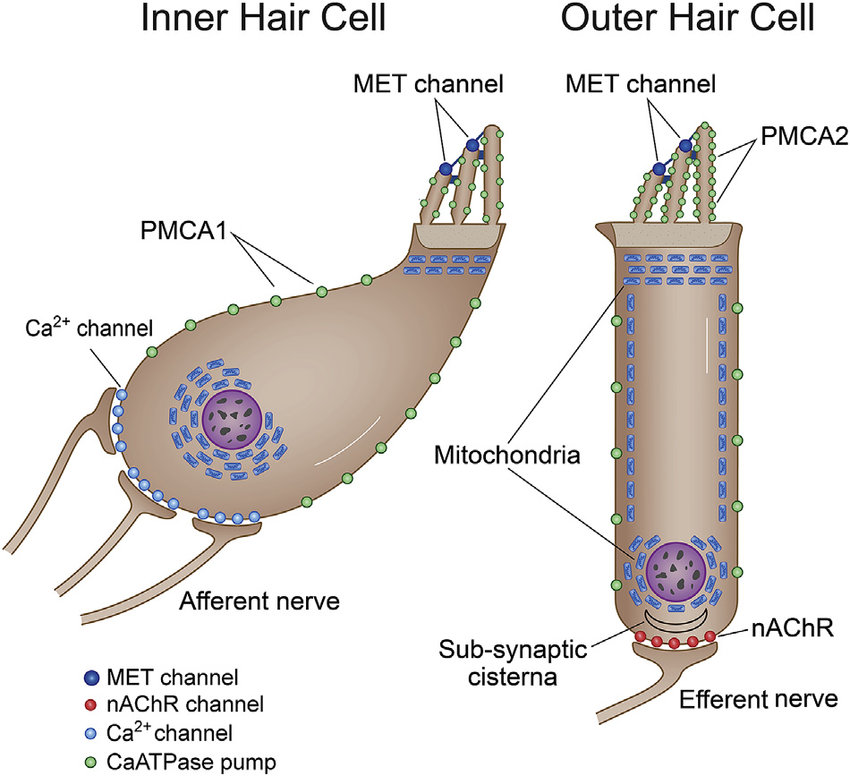
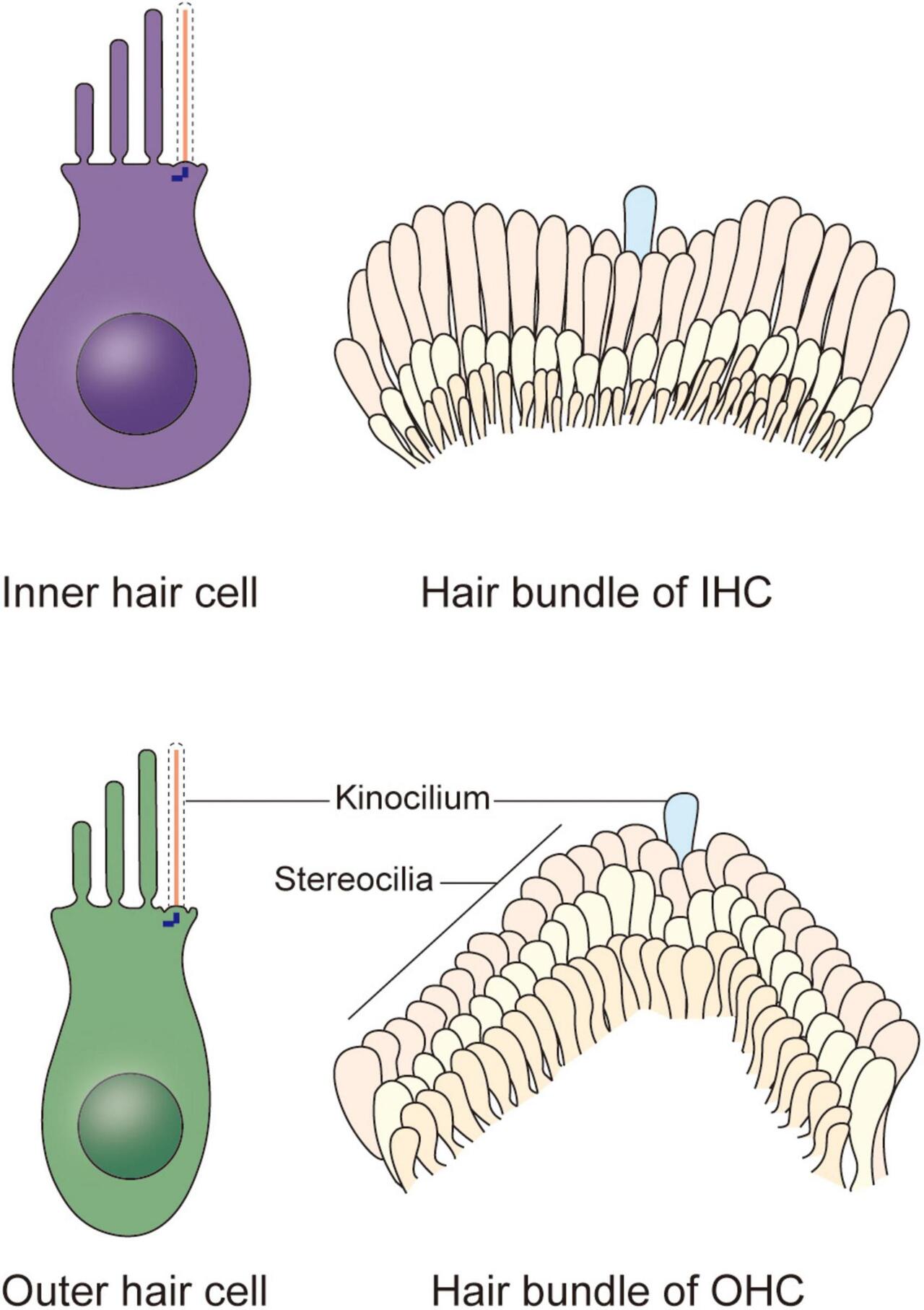
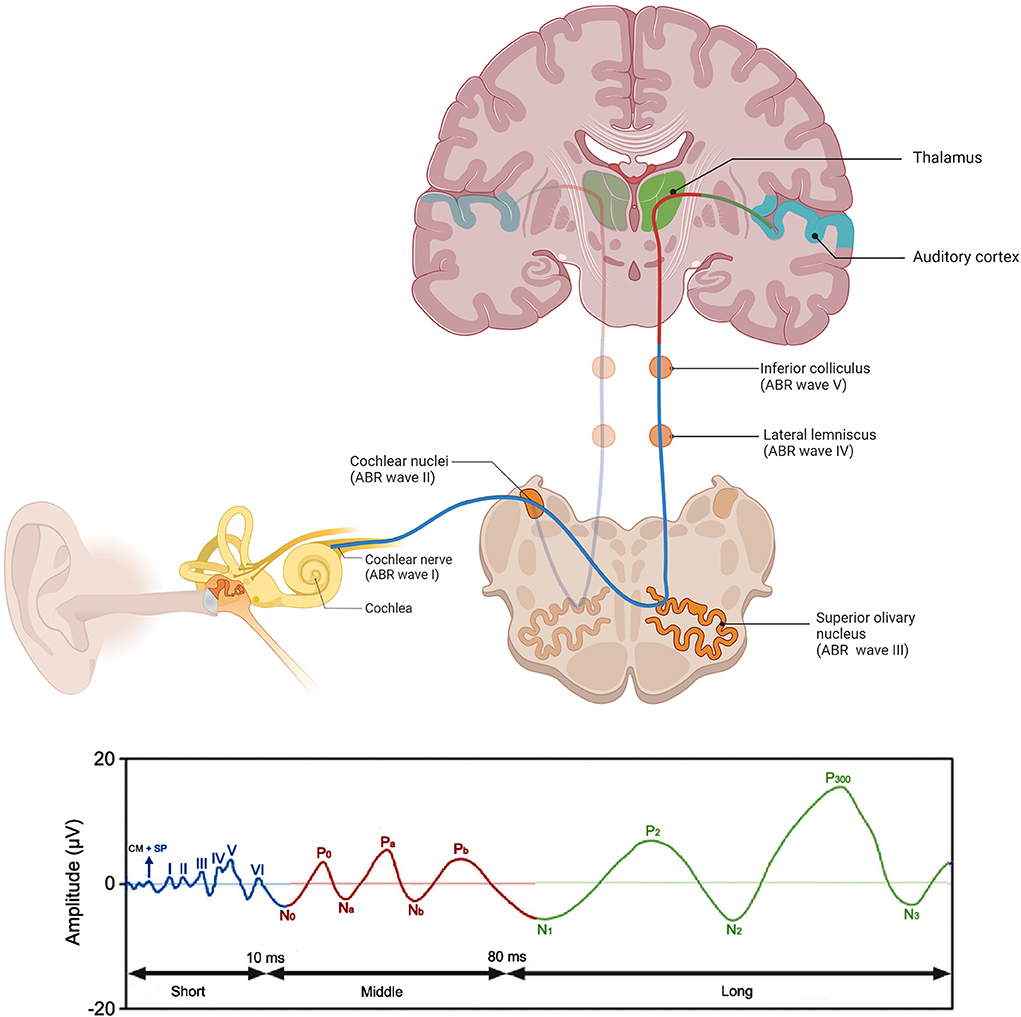
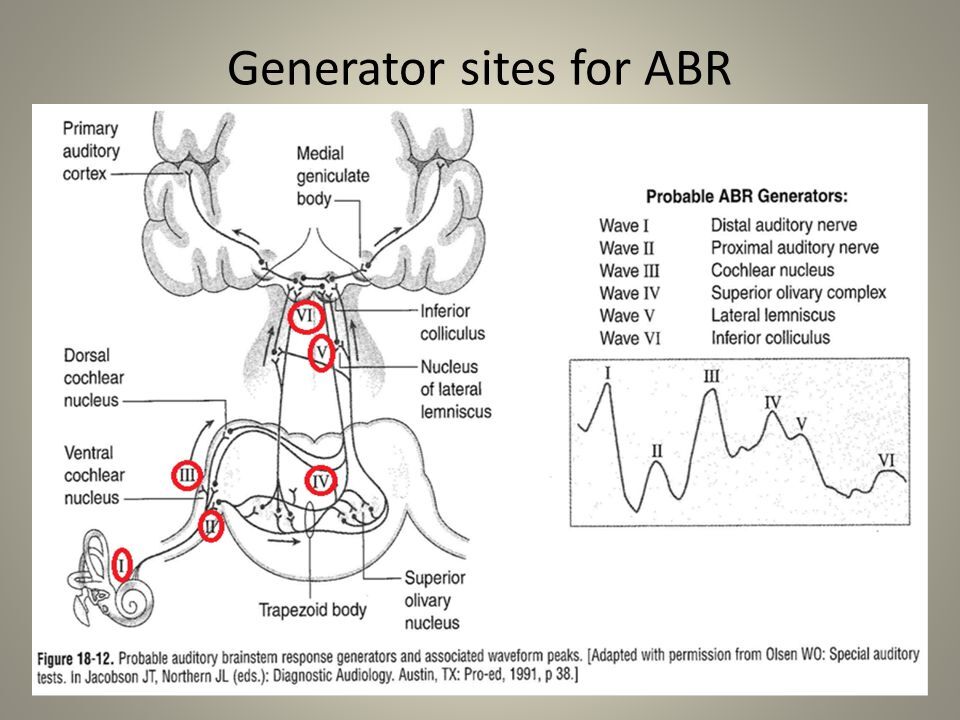
ABR
Auditory brainstem response test (ABR) analysis determines the sound intensity at which a neural response first appears (hearing threshold). The input/output function of wave 1b, which is specifically generated by Type-I SGNs. There are five primary ABR waveform components, waves I through V. Wave I is generated from the distal portion of cranial nerve VIII where it exits the cochlea. When looking at the waveform, we are then able to follow the pathway up through the lower brainstem. Wave I is initiated at the peripheral or distal portion of cranial nerve VIII.
There are five primary ABR waveform components, waves I through V. Wave I is generated from the distal portion of cranial nerve VIII where it exits the cochlea. When looking at the waveform, we are then able to follow the pathway up through the lower brainstem. Wave I is initiated at the peripheral or distal portion of cranial nerve VIII