| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 홍정모님
- 프로그래밍
- standford University
- sizeof()
- compile time constants
- 코드블럭 오류
- #define
- 나동빈님
- 이코테
- decimal
- Machine Learning
- 기계학습 기초
- 코딩테스트
- const
- 연산자
- algorithm
- 본즈앤올
- Greedy
- regression problem
- 기계학습
- classification problem
- coursera
- 학습 알고리즘
- Andrew Ng
- 단항연산자
- #endif
- Runtime constants
- C++
- 형변환
- CLion
- Today
- Total
wellcome_공부일기
Rodent/Mice behavioral experiment 본문
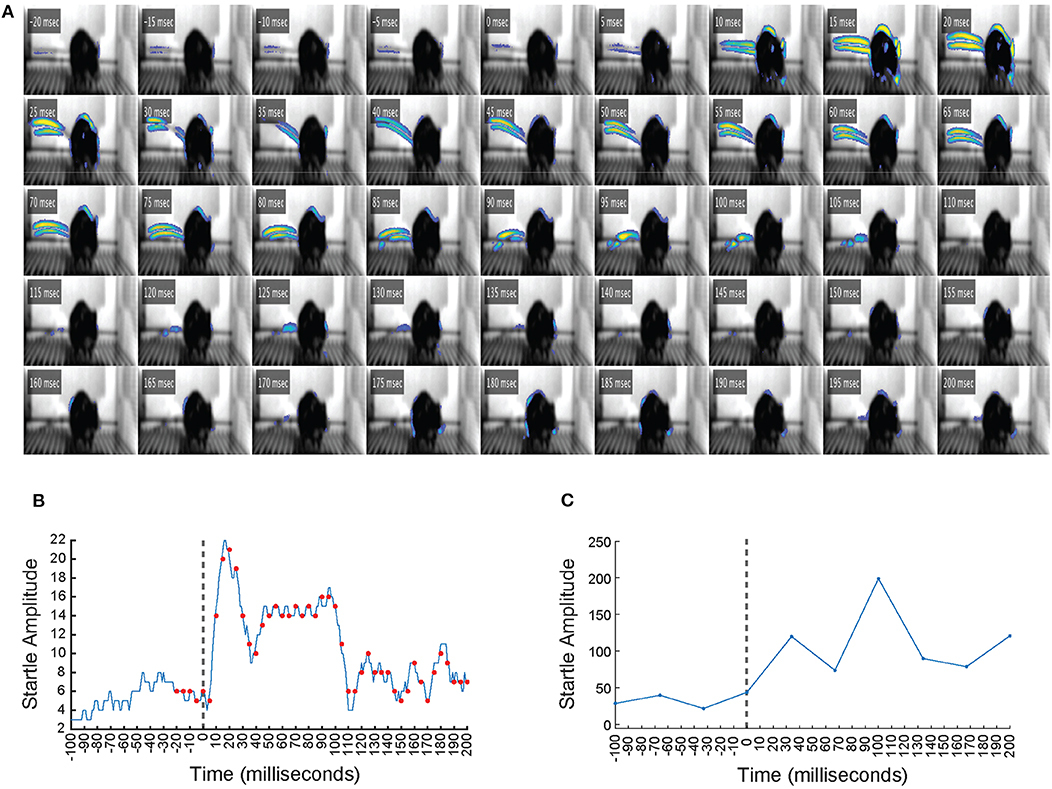
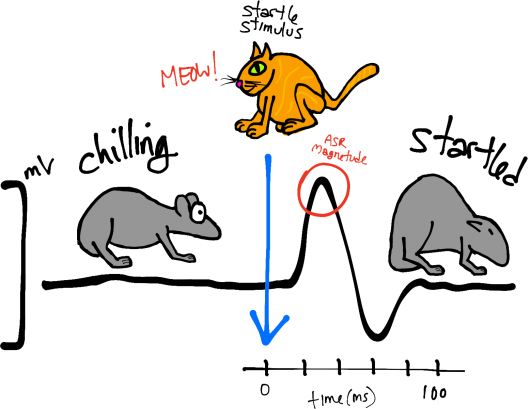
Acoustic startle reflex (ASR)
The acoustic startle reflex (ASR) is actually pretty simple. When mice/rats are surprised by a loud noise (Fig. 1, left; Meow!), their facial and skeletal muscles rapidly contract. This includes closing of the eyes, stiffening of the neck and body (Fig. 1, left; startled mouse), and other physical changes that might protect the animal and help prepare it for a fight/flight response. https://conductscience.com/maze/acoustic-startle-response/
Acoustic Startle Response | Maze Engineers
Basic introduction to Acoustic Startle Reflex with figures to explain the concept. Startle response is a key tool for stimulus-response neural plasticity
conductscience.com
The rodent acoustic startle response is commonly used to study fundamental properties of the central nervous system, including habituation, sensitization, classical conditioning, fear and anxiety, sensorimotor gating, and drug effects (Groves and Thompson, 1970; Davis, 1980, 1986, 2006; Davis et al., 1982, 1993; Swerdlow et al., 1992; Pilz and Schnitzler, 1996; Koch, 1999).