| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- algorithm
- 코딩테스트
- 프로그래밍
- 본즈앤올
- coursera
- #endif
- #define
- 이코테
- compile time constants
- 형변환
- const
- regression problem
- decimal
- 나동빈님
- classification problem
- Andrew Ng
- standford University
- Machine Learning
- C++
- 홍정모님
- 기계학습 기초
- sizeof()
- CLion
- 단항연산자
- 코드블럭 오류
- 학습 알고리즘
- Runtime constants
- 기계학습
- 연산자
- Greedy
- Today
- Total
wellcome_공부일기
02.02. C++ | 정수형(Integer Data Types) 본문
<목차>
1. 정수 자료형(Integer Data Types) 테이블
2. 정수 자료형 구조(signed or unsigned)
3.Short를 이용한 정수 자료형의 Overflow/Underflow
4. 정수 값을 소수점으로 바꾸기
정수 자료형(Integer Data Types) 테이블
사용하는 컴퓨터와 컴파일러에 따라 크기가 다를 수 있으니, 코드로 확인하는게 정확합니다.
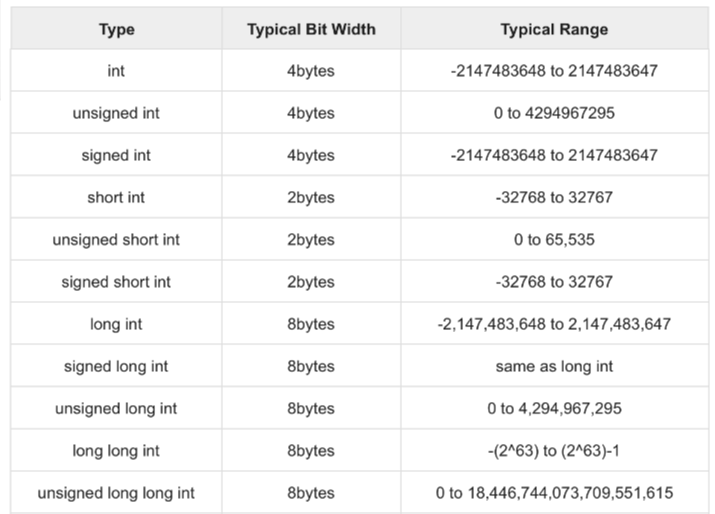
정수 자료형 구조(signed or unsigned)
정수형은 4바이트로 32비트입니다. 컴퓨터는 0과 1로 정보를 저장하므로 총 2^32제곱만큼 사용가능하다는 것을 의미합니다.
맨 앞에 한 비트(Sign bit)는 부호에 사용되는데, 0일때는 양수를 나타내고 1일때는 음수를 나타냅니다.
참고로 위의 표와 같이 unsigned는 0또는 양수를, signed는 음수에서 양수를 나타냅니다.
- 정수 자료형 사이즈 알아보기
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
short s =1;
int i = 1;
long l = 1;
long long ll =1;
cout << sizeof(short) << endl; //output: 2
cout << sizeof(int) << endl; //output: 4
cout << sizeof(long) << endl; //output: 8
cout << sizeof(long long) << endl; //output: 8
return 0;
}
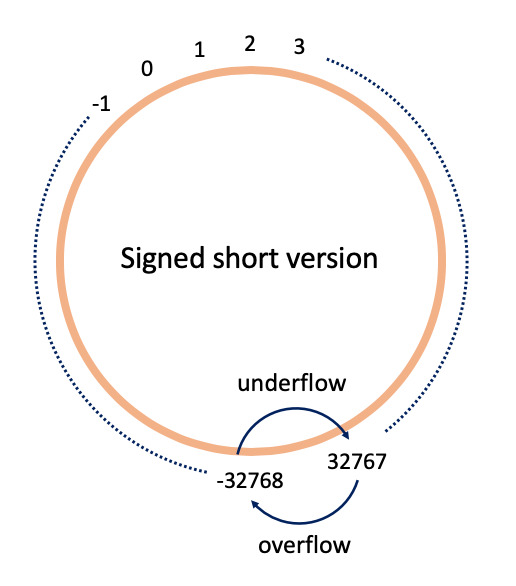
Short를 이용한 정수 자료형의 Overflow/Underflow
정수를 저장할 short는 2바이트로 16비트(2x8)이고, 2^16이 사용가능합니다.
최대 크기를 계산하기 위해서 맨 앞의(Sign bit)를 제외하고 2x7비트로 설정하고 0을 포함하므로 마지막 계산에서 0을 빼줍니다.
최대 32767 최소 -32768이 나오는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.(위의 표를 참고해도 됩니다!)
하지만, 최대 크기에 1을 더하면 overflow가 발생하여 -32768가 출력되고, 최소 크기에 -1을 실행한다면 32767이 나옵니다.
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <limits>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
short s = 1;
cout << pow(2,sizeof(short)*8-1)-1 << endl; //output: 32767 is biggest number
cout << numeric_limits<short>::max() << endl; //output: 32767
cout << numeric_limits<short>::min() << endl; //output: -32768
cout << numeric_limits<short>::lowest() << endl; //output: -32768
s = 32767;
s = s+1;
cout << "32768? : " << s << endl;
s = -32768;
s = s-1;
cout << "-32769? : " << s << endl;
return 0;
}- 제곱 표현을 하기 위해서 math.h 파일에 있는 pow함수 사용하였습니다.
- 최소, 최대 크기 측정을 위해 limits 파일을 사용하였습니다.
- 정수를 저장하였고, (signed) short인 경우입니다.
- 최대 크기에 1을 더하면 overflow가 발생하여 -32768가 출력되고, 최소 크기에 -1을 실행한다면 32767이 나옵니다.
- 정수형 메모리 공간의 한계때문에 숫자 표현 면에서 제한이 있어, overflow or underflow가 발생합니다.
- unsigned라면 최대 크기 65,535에 1을 더하면 0이 나옵니다.
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <limits>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
unsigned int i = -1;
signed int j = -1;
cout << pow(2,sizeof(unsigned int)*8)-1 << endl; //output: 4294967295
cout << numeric_limits<unsigned int>::max() << endl; //output: 4294967295
cout << numeric_limits<unsigned int>::min() << endl; //output: 0
cout << numeric_limits<unsigned int>::lowest() << endl; //output: 0
cout << i << endl; //output: 4294967295
cout << j << endl; //output: -1
return 0;
}- signed는 음수와 양수를 포함하므로 부호를 사용하는 Sign bit를 빼고 계산해야 합니다.
- 만약, unsigned로 할 경우에는 0과 양수만을 표현하므로 Sign bit를 빼지 않고 0만 제외하고 계산하면 됩니다.
정수값을 소수점으로 바꾸기
정수에 둘 중 하나에만 float를 이용하면 소수점까지 출력을 해줍니다. 또한 형변환을 해주면 소수점까지 나오는 걸 확인할 수 있습니다.
하지만 연산자와 같이 저장한 값은 정수만 나오므로 유의해서 사용해야 합니다.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int s = 22/4;
int f = 123445678;
cout << s << endl; //output : 5
cout << (float)s << endl; //output : 5
cout << f << endl; //output : 123445678
cout << (float)f << endl; //output : 1.23446e+08
cout << (float)22/4 << endl; //output : 5.5
cout << 22/(float)4 << endl; //output : 5.5
return 0;
}
* 해당 글은 홍정모님의 따라 배우는 C++을 공부한 토대로 작성되었습니다.
* www.tutorialspoint.com 에서 이론을 공부한 바탕으로 작성되었습니다.
'프로그래밍 > C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 02.04. C++ | 무치형(Void Data Types) = No Type! (0) | 2020.05.05 |
|---|---|
| 02.03. C++ | 고정너비 정수(Fixed-width integers)란? (0) | 2020.05.04 |
| 02.01. C++ | 기본 자료형(Primitive Built-in Types)과 + α (0) | 2020.05.02 |
| 01.11. C++ | 변수 초기화 3가지 방법과 차이 (0) | 2020.04.30 |
| 01.10. C++| 전처리기(Preprocessor)란? (1) | 2020.04.29 |


